What Is Operating Leverage? Formula, Key Points, & Example
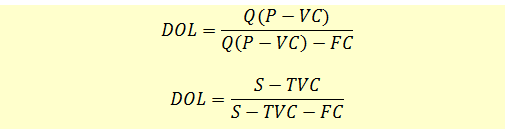
A high DOL can be good if a company is expecting an increase in sales, as it will lead to a corresponding operating income increase. However, a high DOL can be bad if a company is expecting a decrease in sales, as it will lead to a corresponding decrease in operating income. Degree of operating leverage, or DOL, is a ratio designed to measure a company’s sensitivity of EBIT to changes in revenue. This means a 10% increase in sales would lead to a 26.7% increase in operating income.
Do you own a business?

For example, a DOL of 2 means that if sales increase (decrease) by 50%, operating income is expected to increase (decrease) by twice, i.e., 100%. Investors can come up with a rough estimate of DOL by dividing the change in a company’s operating profit by the change in its sales revenue. Even a rough idea of a firm’s operating leverage can tell you a lot about a company’s prospects. In this article, we’ll give you a detailed guide to understanding operating leverage. Understanding DOL allows managers to make informed decisions about pricing, production, and investment by evaluating the potential impact of sales fluctuations on profitability.
Degree of Operating Leverage vs Degree of Combined Leverage
Similarly, the fixed costs of company XYZ and company LMN are $10.9 million and $6.54 million. Degree of combined leverage measures a company’s sensitivity of net income to sales changes. Operating income is equal to sales minus variable costs and fixed costs.
How Does Cyclicality Impact Operating Leverage?
These calculators are important because as critical as it is to know how the business is doing, the price you are paying for a part of the company is also important. We will need to get the EBIT and the USD sales for the two consecutive periods we want to analyze. In this case, it will be the 1st quarter, 2020 and the2nd quarter, 2020. The catch behind having a higher DOL is that for the company to franchisor accounting software receive positive benefits, its revenue must be recurring and non-cyclical. Furthermore, another important distinction lies in how the vast majority of a clothing retailer’s future costs are unrelated to the foundational expenditures the business was founded upon. However, the finance manager should carefully consider the situation and make a decision that enhances the benefits to shareholders.
- That’s why we highly recommend you check out our otherfinancial calculators.
- EPS would have declined by 33.3% (i.e., DFL of 1.11 x -30% change in EBIT).
- The revenues of company XYZ are $ 58.6 million, and that of company LMN are $ 32.7 million.
- Specifically, DOL is the percentage change in income (usually taken as earnings before interest and tax, or EBIT) divided by the percentage change in the level of sales output.
Operating leverage vs. financial leverage
That indicates to us that this company might have huge variable costs relative to its sales. Similarly, we can conclude the same by realizing how little the operating leverage ratio is, at only 0.02. When the company makes more investments in fixed costs, the increase in revenue does not affect the fixed costs. The fixed cost per unit decreases, and overall operating profits are increased. A measure of this leverage effect is referred to as the degree of operating leverage (DOL), which shows the extent to which operating profits change as sales volume changes. This indicates the expected response in profits if sales volumes change.
Great! The Financial Professional Will Get Back To You Soon.
Managers use operating leverage to calculate a firm’s breakeven point and estimate the effectiveness of pricing structure. An effective pricing structure can lead to higher economic gains because the firm can essentially control demand by offering a better product at a lower price. If the firm generates adequate sales volumes, fixed costs are covered, thereby leading to a profit. However, to cover for variable costs, a firm needs to increase its sales. If fixed costs are higher in proportion to variable costs, a company will generate a high operating leverage ratio and the firm will generate a larger profit from each incremental sale.
For example, in a company with high DOL, a 10% increase in sales could lead to a more than 10% increase in EBIT, magnifying the impact on profitability. This leverage can be advantageous during periods of rising sales but poses higher risks during downturns. In fact, the relationship between sales revenue and EBIT is referred to as operating leverage because when the sales level increases or decreases, EBIT also changes. Most of Microsoft’s costs are fixed, such as expenses for upfront development and marketing.
There are many alternative ways of calculating the degree of operating leverage. Operating leverage is the most authentic way of analyzing the cost structure of any business. There are many different methods to do the financial analysis of a company. Ratio analysis is the most commonly used method for assessing a firm’s financial health, profitability, and riskiness. Yes, DOL can be used to compare the operational risk of companies within the same industry, helping investors identify firms with higher or lower financial risk profiles.



