Labor Efficiency Variance
The term “purchase price variance,” or PPV variance, is used to show the difference between the estimated and actual costs in accounting. Direct materials price variance account is a contra account that is debited to record the difference between the standard price and actual price of purchase. Materials price variance represents the difference between the standard cost of the actual quantity purchased and the actual cost of these materials.
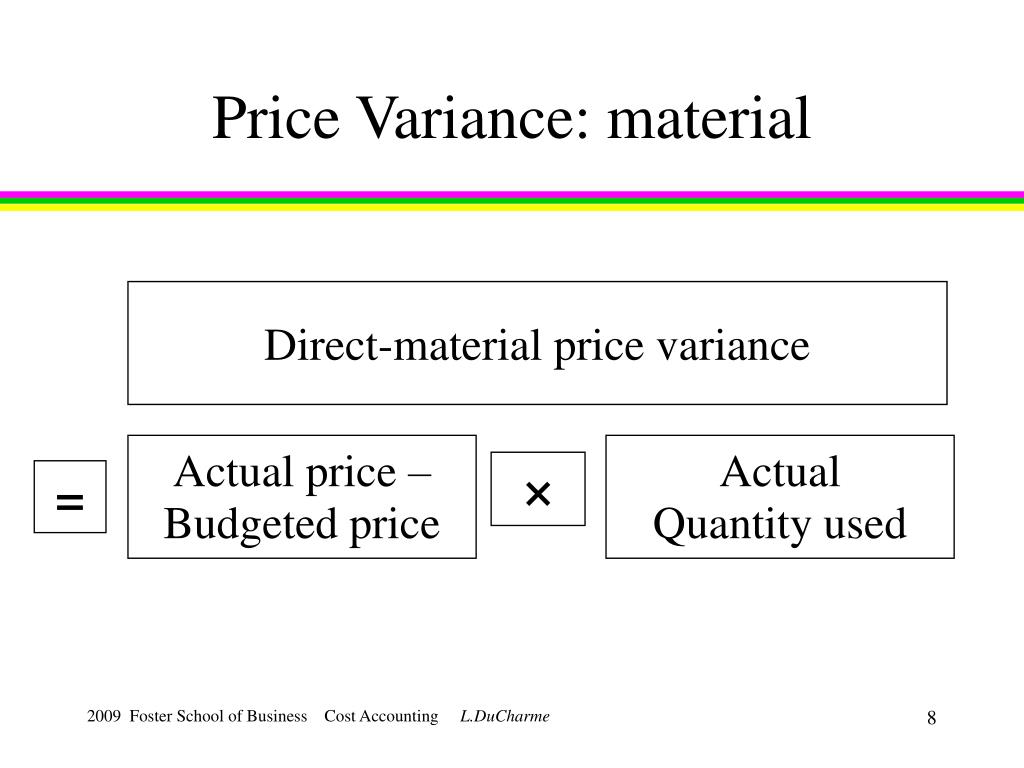
Formula(s) to Calculate Direct Material Price Variance
The difference between the standard cost of direct materials specified for production and the actual cost of direct materials used in production is known as Direct Material Cost Variance. Materials price variance (or direct materials price variance) is the part of materials cost variance that is attributable to the difference between the actual price paid and the standard price specified for direct materials. Premium Furniture, a US based Inc., uses a standard costing system to control its direct materials and conversion costs. During the month of December 2022, its workers used 3,750 feet of timber to finish 1,500 office chairs. The standard length of timber allowed to manufacture an office chair is 2.75 feet and the standard rate per foot of timber is $3.50.
- With our direct material price variance calculator, we aim to help you assess the difference between the actual cost of direct materials and the standard cost.
- This involves looking beyond the numbers to understand the underlying factors contributing to the variances.
- In other words, if the business has consumed fewer materials to produce a given level of output than expected, the material quantity variance is said to be favorable.
- He has served in various leadership roles in the American Bar Association and as Great Lakes Area liaison with the IRS.
What is direct material price variance?
Conversely, issues such as late deliveries, substandard materials, or unexpected price hikes can lead to variances. Building strong relationships with suppliers and regularly evaluating their performance can help businesses anticipate and address potential problems before they impact production. Together with the price variance the quantity variance forms part of the total direct materials variance. For budgeting purposes, many companies determine a standard cost at the beginning of each year that is used as the estimated price of goods throughout the year.

Why You Can Trust Finance Strategists
Total actual and standard direct materials costs are calculated by multiplying quantity by price, and the results are shown in the last row of the first two columns. When complete, capitalizable variances should be recorded in a “standard-to-actual” reserve within inventory on the balance sheet with the remainder being appropriately expensed through the income statement. This reserve has the effect of adjusting the company’s inventory balances to “actual,” which is appropriate under GAAP. On a net basis, the purchase price variance is really the difference between standard cost of the material and the actual invoice price of the material. The materials price variance can be computed either when materials are purchased or when they are placed into production. The standard rates calculated for batch and product level activities do not vary with production volume.
The difference between this actual expenditure and the actual expenditure on direct material is the direct materials price variance. The standard price of materials purchased by Angro is $2.00 per kg and standard quantity of materials allowed to produce a unit of product is 1.5kg. Calculate direct materials quantity variance and also indicate whether it is favorable or unfavorable.
How to Compute Direct Materials Variances
Direct materials quantity variance is a part of the overall materials cost variance that occurs due to the difference between the actual quantity of direct materials used and the standard quantity allowed for the output. Generally, the production managers are considered responsible for direct materials quantity variance because they are the persons responsible for keeping a check on excessive usage of production inputs. However, purchase managers may purchase low quality, substandard or otherwise unfit materials with an intention to improve turbotax mobile app, do your taxes on your phone, tablet, or computer direct materials price variance. In such cases, the responsibility of any unfavorable quantity variance would lie on the purchasing department. Irrespective of who appears to be responsible at first glance, the variance should be brought to the attention of concerned managers for quick and timely remedial actions. As is the case when analyzing other variances, the direct material price variance needs to be assessed in the context of other relevant variances and factors, such as direct material price variance and direct labor variances.
Like direct materials price variance, this variance may be favorable or unfavorable. If workers manufacture a certain number of units using a quantity of materials that is less than the quantity allowed by standards for that number of units, the variance is known as favorable direct materials quantity variance. On the other hand, if workers use the quantity that is more than the quantity allowed by standards, the variance is known as unfavorable direct materials quantity variance. To compute the direct materials price variance, subtract the actual cost of direct materials ($297,000) from the actual quantity of direct materials at standard price ($310,500). This difference comes to a $13,500 favorable variance, meaning that the company saves $13,500 by buying direct materials for $9.90 rather than the original standard price of $10.35.
This example illustrates the accounting entries for purchase price variance and exchange rate variance for a standard cost item. An adverse or unfavorable material quantity variance occurs when the actual volume of materials used in production exceeds the standard quantity that is expected for the level of output in a period. This involves looking beyond the numbers to understand the underlying factors contributing to the variances. For example, if a material price variance is detected, managers should examine market conditions, supplier performance, and procurement strategies to pinpoint the cause. Similarly, if a material quantity variance is found, a thorough review of the production process, employee performance, and equipment efficiency is necessary.



